Note| Text in Blue [#PYTHON], Rose [#PROTRACTOR], Red [#RUBY] and Orange [#JAVA] can be edited or mentioned important for the entire blog. All the posts are practically done by me.
Experimental CSS Locators in automation aspects
Note: This post is fully experimented on https://www.python.org/
General
ID
#id-search-field
The same can be achieved through,
*#id-search-field
input#id-search-field
The same can be achieved through,
*#id-search-field
input#id-search-field
Class
.search-field
.search-field.placeholder
.search-field.placeholder
The same can be achieved through,
*.search-field
input.search-field
Direct Child | absolute css
'>' operator matches the immediate child of an element
.python.home > #touchnav-wrapper > #nojs > p > strong:contains(Notice:)
.python.home > #touchnav-wrapper > #nojs > p > strong:contains(Notice:)
Sub Child | relative css
a space between two instance matches any descendant of a parent/grand-parent elements
.python.home strong:contains(Notice:)
.python.home strong:contains(Notice:)
contains | text
locates elements with text
button:contains(GO)
button:contains(GO)
not contains | text
Attrribute
CSS locates elements using properties
input[name='q']
input[name='q']
input[id='id-search-field']
input[class='search-field placeholder']
input[class='search-field placeholder'][id='id-search-field']
.tier-2:contains(Group):not([class*='element-4'])
input[class='search-field placeholder']
input[class='search-field placeholder'][id='id-search-field']
not contains | attribute
locates all the elements that doesn't contain specific property, text, etc.,
.tier-2:contains(Group):not(.element-4)locates all the elements that doesn't contain specific property, text, etc.,
.tier-2:contains(Group):not([class*='element-4'])
Advanced attrribute css selectors
CSS locates dynamic elements using the following operators
= operator
= operator
~= operator
^= operator
$= operator
^= operator
$= operator
*= operator
|= operator
|= operator
Equal
= operator lets you find elements that matches attribute with the exact specified value
*[class='python home']= operator lets you find elements that matches attribute with the exact specified value
space-separated values
~= operator lets you find elements that matches attribute with space-separated values
*[class~='menu']~= operator lets you find elements that matches attribute with space-separated values
prefix [begins-with]
^= operator lets you find elements that matches attribute starting with the specified value
*[class^='main']^= operator lets you find elements that matches attribute starting with the specified value
suffix [ends-with]
$= operator lets you find elements that matches attribute ending with the specified value
*[class$='home']$= operator lets you find elements that matches attribute ending with the specified value
contains [contains]
*= operator lets you find elements that matches attribute with a specified value, which is a part of actual attribute value
*[class*='shell']*= operator lets you find elements that matches attribute with a specified value, which is a part of actual attribute value
hyphen separated values
|= operator lets you find elements that matches attribute with hyphen-separated values starting from the left
*[class|='site']|= operator lets you find elements that matches attribute with hyphen-separated values starting from the left
Css Siblings
CSS locates sibilings similar to xpath
Next sibling
General sibling
Next sibling
General sibling
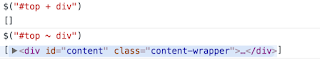
Next or Adjacent sibling
selects the element/sibling next to the current element
#top + headerGeneral sibling
selects any number of siblings with matching type coming next to next from the current element
#top ~ div
Pseudo class
Pseudo-classes are actually not css inborn instead they are an absolute CSS foreigners implemented through JQuery, mootools, etc., listed below are some of the most commonly used pseudo classes for automation,
:nth()
:nth-child()
:first-child
:last-child
:first-of-type
:last-of-type
:nth-of-type()
:only-of-type
hover
E:focus
link
visited
.meta-navigation.container *:nth(0)
here, it selects all the first child elements of the type <li>
[role='menubar'] li:nth-child(1)
first-of-type
last-of-type
:nth()
:nth-child()
:first-child
:last-child
:first-of-type
:last-of-type
:nth-of-type()
:only-of-type
hover
E:focus
link
visited
nth()
collects the entire child, sub-child of a parent and matches the list in a sequential order or index with value starting from 0 as count 1
.main-header .container div:nth(2).meta-navigation.container *:nth(0)
nth-child()
unlike nth(), nth-child filters only the child with type and location
[role='menubar'] *:nth-child(1)here, it selects all the first child elements of the type <li>
[role='menubar'] li:nth-child(1)
first-child
first-child is similar to nth-child(1)
[role='menubar'] li:first-child
last-child
last-child is similar to first-child but locates the child's last elements
[role='menubar'] li:last-childfirst-of-type
locates the parent's first elements w.r.t type
[role='menubar'] li:first-of-typelast-of-type
locates the parent's last elements w.r.t type
[role='menubar'] li:last-of-type
only-of-type
matches all the given type (say, h1 tag) under a specific element
.main-header .container h1:only-of-type
hover
locates element on hover over
*[href='/psf/membership/']:hover
E:focus
locates element on focus
*[href='/psf/membership/']:focus
link
locates element if hyperlinked
*[href='/psf/membership/']:link
visited
locates already visited hyperlink
*[href='/psf/membership/']:visited